Antwort What happens when cells don’t communicate? Weitere Antworten – Why do cells need to communicate
In single-celled organisms, signaling allows populations of cells to coordinate with one another and work like a team to accomplish tasks no single cell could carry out on its own. The study of cell signaling touches multiple biological disciplines, such as developmental biology, neurobiology, and endocrinology.When cells do not respond to the signals that regulate their growth, they are called cancer cells. Cancer is a disorder in which the body's cells could no longer control growth. As a result, these cells replicate uncontrollably and form tumors, which are masses that can damage other tissues that surround it.To enhance communication between cells, a researcher might increase cell-to-cell direct contact or enhance chemical signaling. This could be done by enhancing actions of cell adhesion molecules or gap junctions, or increasing the effectiveness of chemical signals and signal transduction pathways.
What are the ways that cells can communicate with one another : Cells typically communicate using chemical signals. These chemical signals, which are proteins or other molecules produced by a sending cell, are often secreted from the cell and released into the extracellular space. There, they can float – like messages in a bottle – over to neighboring cells.
Why is cell cell interaction important
Cell–cell interaction refers to the direct interactions between cell surfaces that play a crucial role in the development and function of multicellular organisms. These interactions allow cells to communicate with each other in response to changes in their microenvironment.
What happens to cells that do not have enough energy : Hardest hit are organs and tissues that need a lot of energy, like muscles, brain, heart, kidneys and liver. When the energy supply slumps, cells can become damaged or destroyed.
Because cancer cells ignore the body's signals to stop dividing, they start invading tissues nearby. If a tumor is benign, it may push up against neighboring tissues, but won't invade it. However, a malignant tumor invades tissue and is capable of spreading throughout the body.
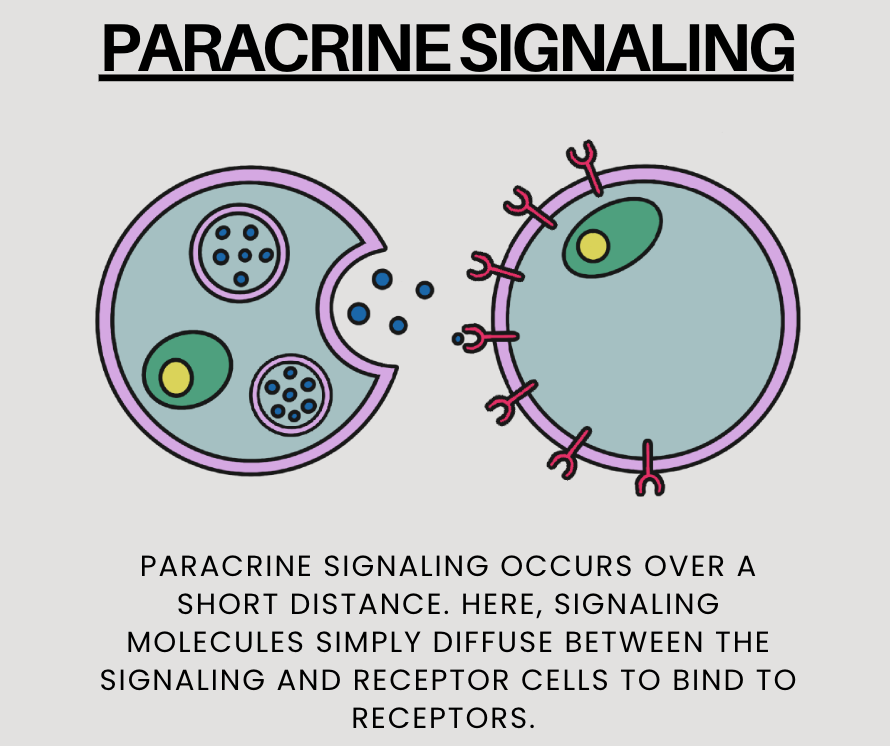
In multicellular organisms, growth factors, hormones, neurotransmitters, and extracellular matrix components are some of the many types of chemical signals cells use. These substances can exert their effects locally, or they might travel over long distances.
What influences how cells communicate
Cell A needs to secrete the signal. These signalling molecules, which are also called ligands, act like a postman bringing that message to its destination. The signalling molecule could be a protein, a lipid, hormones, growth factors or even neurotransmitters.Cell–cell interaction refers to the direct interactions between cell surfaces that play a crucial role in the development and function of multicellular organisms. These interactions allow cells to communicate with each other in response to changes in their microenvironment.Often, the signaling cell and target are different cell types. Cells, however, can also send signals to other cells of the same type, as well as to themselves. In such autocrine signaling, a cell secretes signal molecules that can bind back to its own receptors.
In order to respond to changes in their immediate environment, cells must be able to receive and process signals that originate outside their borders. Individual cells often receive many signals simultaneously, and they then integrate the information they receive into a unified action plan.
Why is it important for cells to be different from each other : Multicellular organisms need many different types of cells to carry out the same life processes. Each of these special types of cells has a different structure that helps it perform a specific function.
What happens if cells don’t receive oxygen : If cells are deprived of glucose and oxygen, cells will die through necrosis. Interestingly, cells remain viable in hypoxia.
What happens if your mitochondria stops working
The mitochondria's main function is to produce energy. More mitochondria are needed to make more energy, particularly in high-energy demand organs such as the heart, muscles, and brain. When the number or function of mitochondria in the cell are disrupted, less energy is produced and organ dysfunction results.
Disruption of normal regulation of the cell cycle can lead to diseases such as cancer. When the cell cycle proceeds without control, cells can divide without order and accumulate genetic errors that can lead to a cancerous tumor .In order for our bodies to grow and develop, they must produce new cells—and allow for the death of old cells. Cell division is also an essential component of injury repair. If our cells couldn't divide and create new cells, our bodies could never produce new skin cells to heal road rash, or grow a fingernail back.
What cell is responsible for communication : Neurons
Neurons are the cells within the brain that are responsible for rapid communication of information. Although similar to other cells in the body, neurons are specialized in ways that set them apart from other cells and endow them with the properties that allow them to carry out their unique role in the nervous system.