Antwort What are the three ways cells communicate? Weitere Antworten – What are 3 ways cells communicate
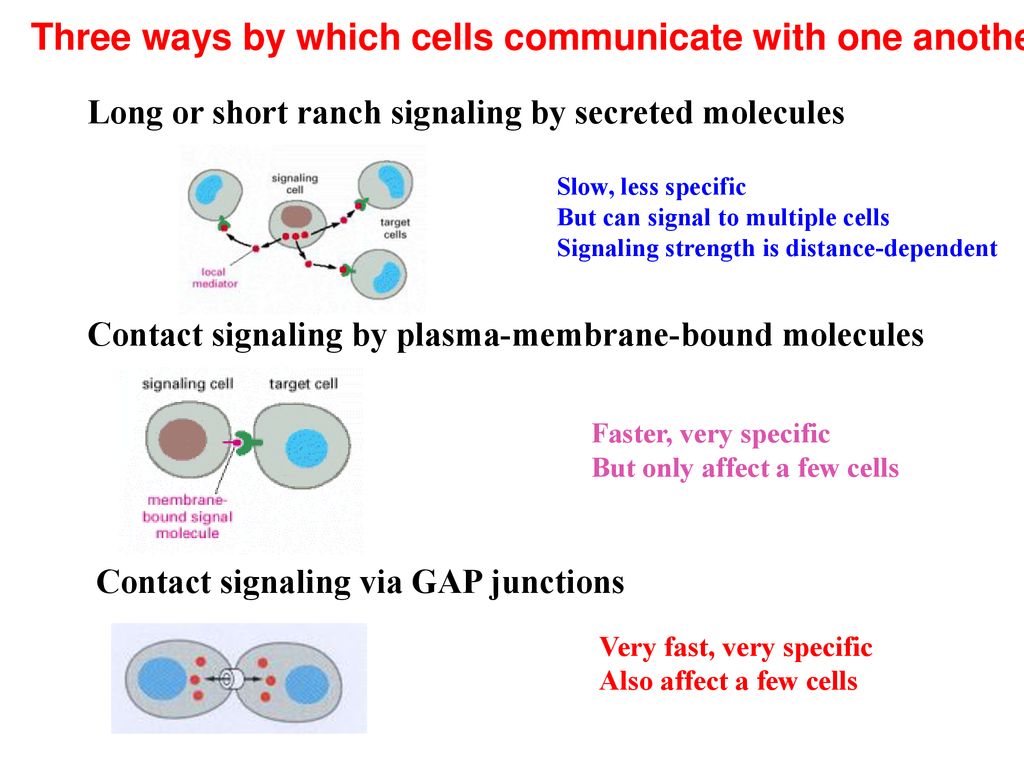
The three main ways for cells to connect with each other are: gap junctions, tight junctions, and desmosomes. These types of junctions have different purposes, and are found in different places.Communication between cells is called intercellular signaling, and communication within a cell is called intracellular signaling.Cells communicate by sending and receiving signals. Signals may come from the environment, or they may come from other cells. In order to trigger a response, these signals must be transmitted across the cell membrane. Sometimes the signal itself can cross the membrane.

What is the process which cells communicate to each other : Cells typically communicate using chemical signals. These chemical signals, which are proteins or other molecules produced by a sending cell, are often secreted from the cell and released into the extracellular space. There, they can float – like messages in a bottle – over to neighboring cells.
What are the 3 parts of cell signaling
Cell signaling can be divided into 3 stages.
- Reception: A cell detects a signaling molecule from the outside of the cell.
- Transduction: When the signaling molecule binds the receptor it changes the receptor protein in some way.
- Response: Finally, the signal triggers a specific cellular response.
What are the 3 ways a cell can respond to a signal : The three steps of signal transduction are: Signal reception using receptor proteins on the cell surface. Transduction of the signal through proteins inside the cell. The cellular response, such as growth, motility, or changes in gene expression.
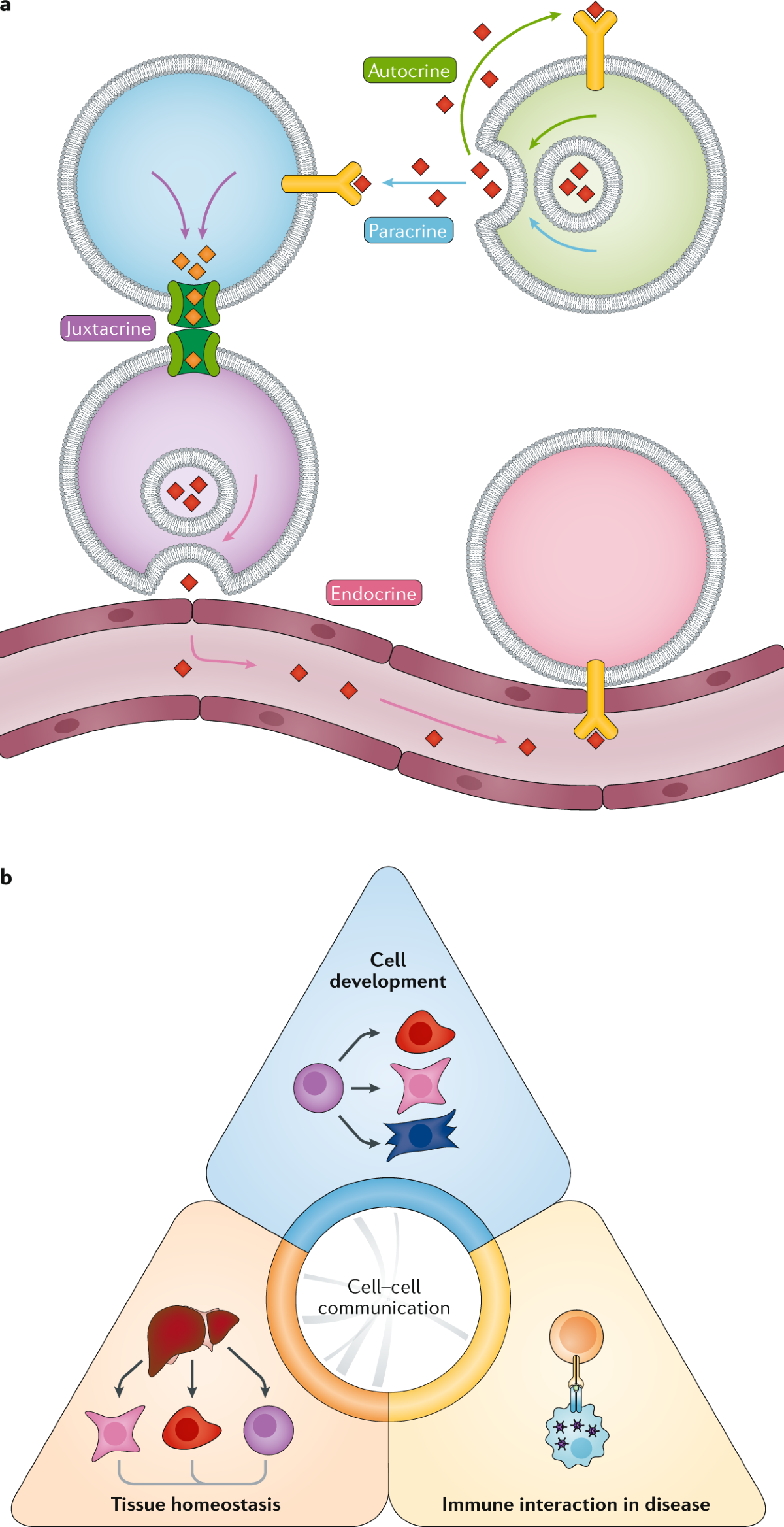
There are four categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, autocrine signaling, and direct signaling across gap junctions.
Tight junctions (blue dots) between cells are connected areas of the plasma membrane that stitch cells together. Adherens junctions (red dots) join the actin filaments of neighboring cells together. Desmosomes are even stronger connections that join the intermediate filaments of neighboring cells.
How do cells communicate simplified
Lesson Summary
Overall, cell communication is a process where a cell is able to influence the behavior of other cells through signaling mechanisms and receiving mechanisms. This process occurs across what is called the signal transduction pathway. The cell which sends a message is called a signaling cell.There are four categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: autocrine signaling, paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and direct signaling across gap junctions (Figure 9.2).A cell is a geographical area covered by the frequency emitted by a base station in a cellular network. The elements that transmit this frequency is called a cell site.
Let's talk about the general sequence of cell. Signaling. First reception typically a signal molecule binds a receptor. Second transduction the receptor gets activated by this binding.
What are the three steps to cell communication and signaling : There are three main steps in the signal transduction pathway:
- Reception – The cell senses a change in the environment.
- Transduction – The signal is sent through the cell.
- Response – There is a change in cellular behavior.
What are the 3 main types of cell theory : The three principles of cell theory are:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
How do cells communicate examples
Two examples of instances of cell communication include: Nerve cells are involved in what is called long-distance signaling. During this process a nerve cell produces a neurotransmitter which is diffused across a synapse or a point where one neuron is touching another. The neurotransmitter then signals the target cell.
The cell cycle is composed of 3 main stages:
- Interphase. During the interphase stage of the cell cycle, the cell grows and organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes double.
- Mitosis. During mitosis, the nucleus membrane degenerates.
- Cytokinesis.
The generally accepted parts of modern cell theory include: All known living things are made up of one or more cells. All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
What are the 3 parts of the cell theory quizlet : List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory.
- All cells come from existing cells.
- Cell is the basic unit of all living things.
- All organisms are composed of 1 or more cells.