Antwort How do cells send signals? Weitere Antworten – How do cells communicate
Intercellular communications in multicellular organisms arise via four different molecular mechanisms: (1) cytoplasmic bridges, (2) exosomes and ectosomes, (3) direct interactions between membrane proteins of adjacent cells, and (4) soluble messenger molecules (mediators) controlling more or less distant target cells.Cells may be self-sustaining units of life, but they don't live in isolation. Their survival depends on receiving and processing information from the outside environment, whether that information pertains to the availability of nutrients, changes in temperature, or variations in light levels.Cells typically receive signals in chemical form via various signaling molecules. When a signaling molecule joins with an appropriate receptor on a cell surface, this binding triggers a chain of events that not only carries the signal to the cell interior, but amplifies it as well.
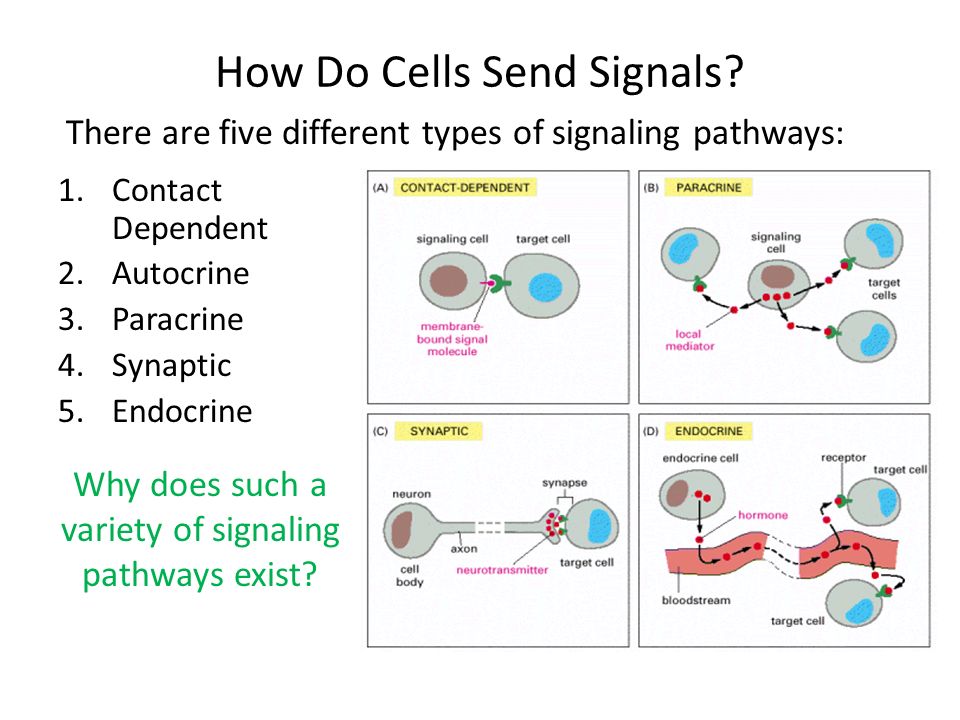
What are the 4 ways cells communicate : Forms of signaling
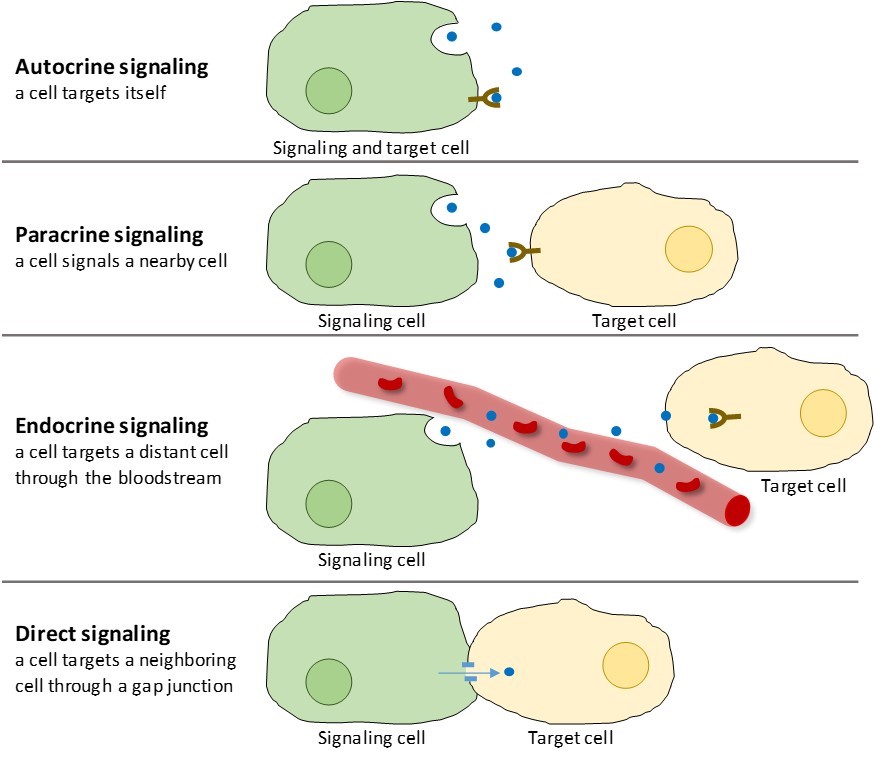
There are four basic categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, autocrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and signaling by direct contact.
How do cells respond to signals
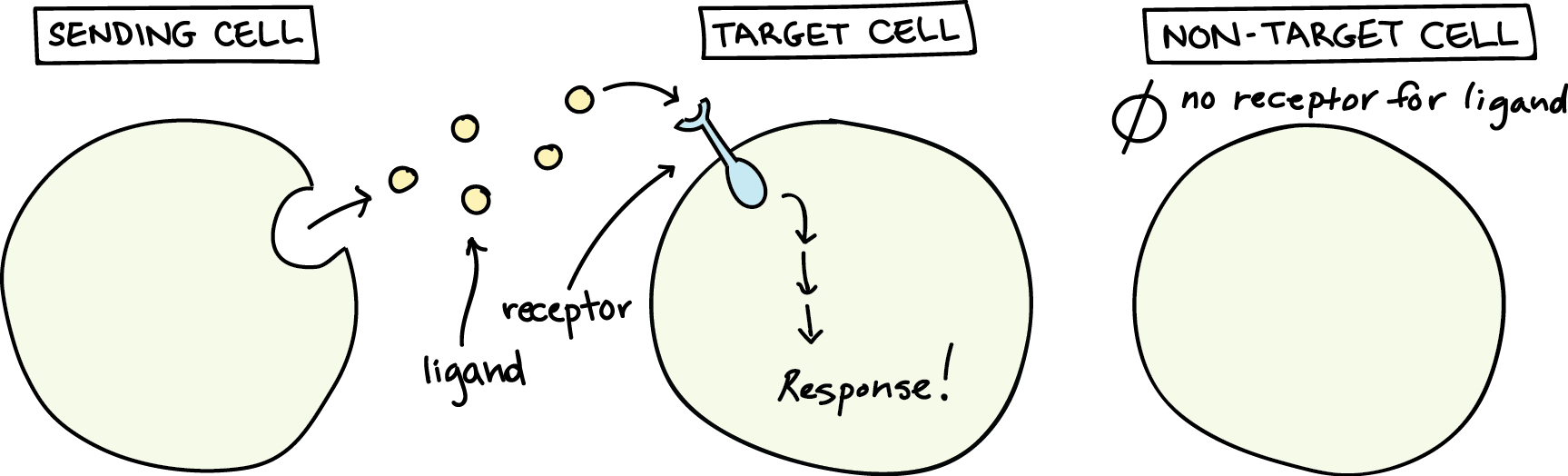
Regardless of the nature of the signal, the target cell responds by means of a specific protein called a receptor, which specifically binds the signal molecule and then initiates a response in the target cell.
Why do cells communicate : Communication is a must during the whole life of an organism, so cells and tissues can alert their neighbours about any needs or information they have like "I need some oxygen over here", "I am an eyeball, so you don't need to be" or "I need some help, bacteria are attacking me”.
Cells communicate by sending and receiving signals. Signals may come from the environment, or they may come from other cells. In order to trigger a response, these signals must be transmitted across the cell membrane. Sometimes the signal itself can cross the membrane.
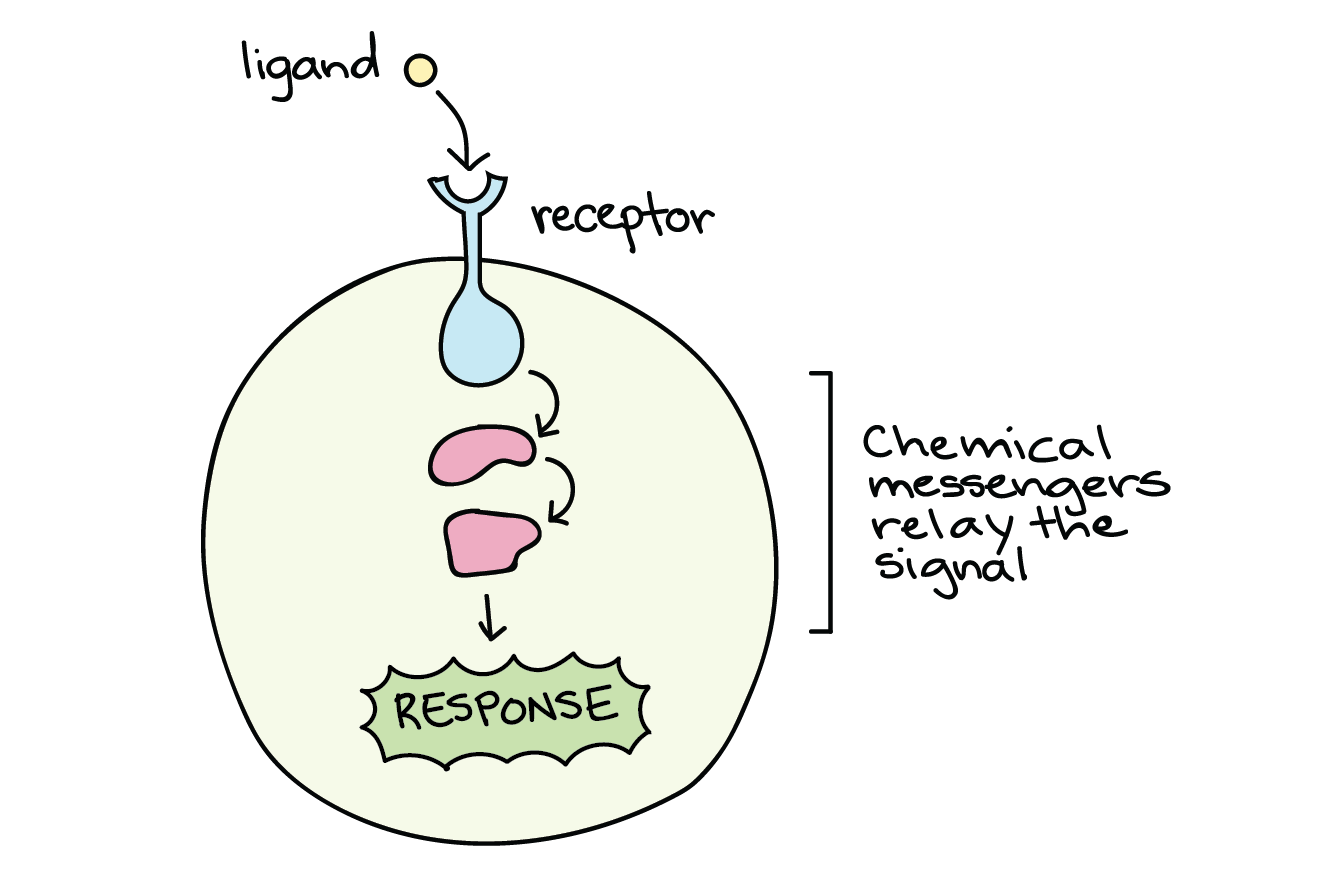
The three stages of cell communication (reception, transduction, and response) and how changes couls alter cellular responses. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
How do cells communicate 3 ways
The three main ways for cells to connect with each other are: gap junctions, tight junctions, and desmosomes.Cells do not respond to every signal. Cells only respond to signals that they have the receptors to detect. This is how specificity occurs even though all cells in the body are exposed to the same hormones in the blood. Cell signals in the environment bind to receptors on the surface of cells.There are four basic categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, autocrine signaling, endocrine signaling, and signaling by direct contact.
Cell signaling can be divided into five major steps: production of the signal, reception, signal transduction, response, and termination of the signal.
What are the 3 ways a cell can respond to a signal : The three steps of signal transduction are: Signal reception using receptor proteins on the cell surface. Transduction of the signal through proteins inside the cell. The cellular response, such as growth, motility, or changes in gene expression.
What are the 3 stages of how cells respond to signals : The three stages of cell communication (reception, transduction, and response) and how changes couls alter cellular responses.
What is cell signaling and how does it work
Cell communication is a crucial biological process where cells interact directly or signal over distances. Direct contact involves gap junctions or complementary surface proteins.

Cell signaling can be divided into 3 stages.
- Reception: A cell detects a signaling molecule from the outside of the cell.
- Transduction: When the signaling molecule binds the receptor it changes the receptor protein in some way.
- Response: Finally, the signal triggers a specific cellular response.
Lesson Summary
Overall, cell communication is a process where a cell is able to influence the behavior of other cells through signaling mechanisms and receiving mechanisms. This process occurs across what is called the signal transduction pathway. The cell which sends a message is called a signaling cell.



